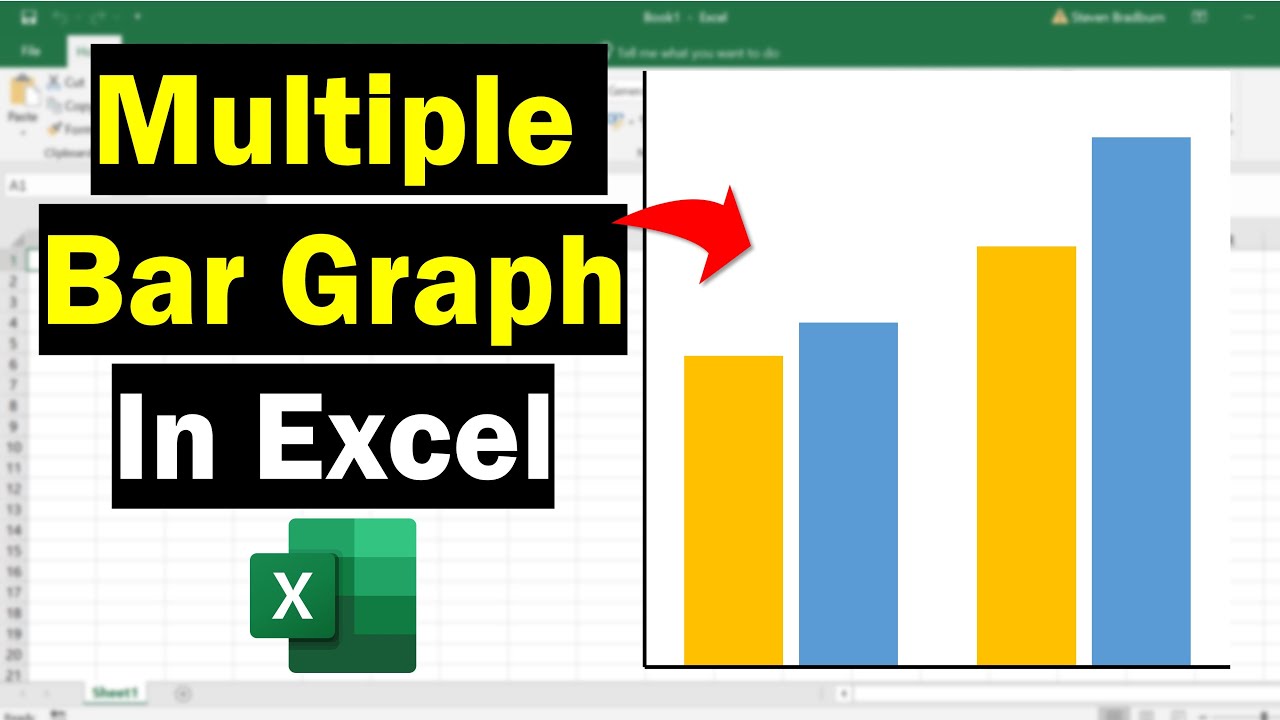
Fantastic Info About How To Draw A Multiple Bar Diagram X And Y Lines On Graph
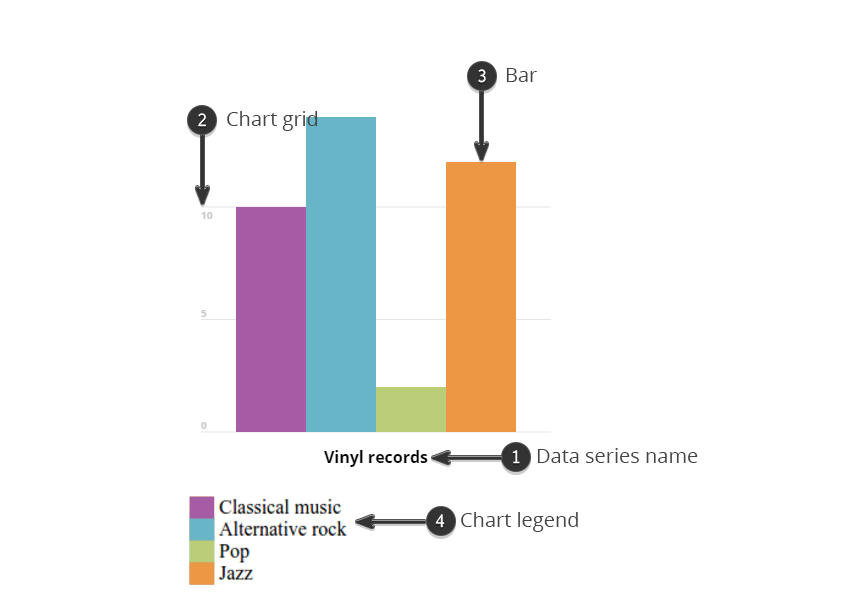
Draw a series of parallel bars for each category.
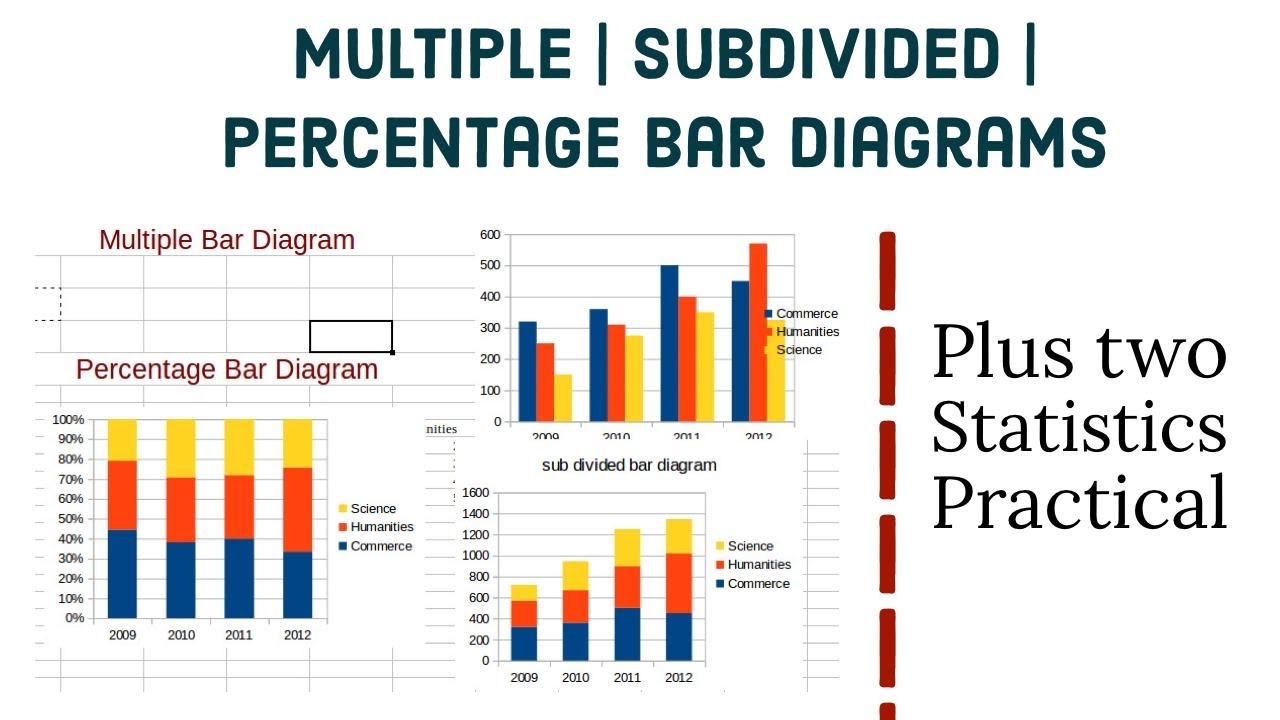
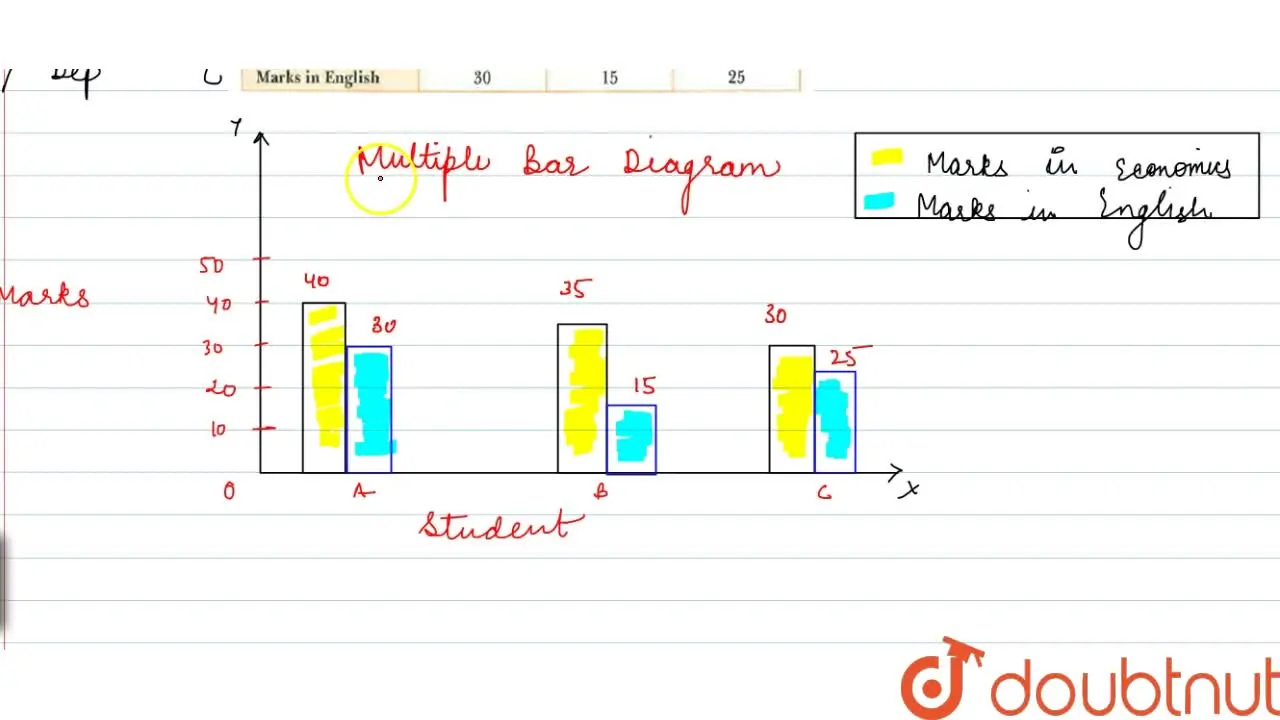
How to draw a multiple bar diagram. First let’s run some code to create an example dataset and set the theme for our charts. Difference between bar graph and pie chart. Understand relationships between categorical variables.
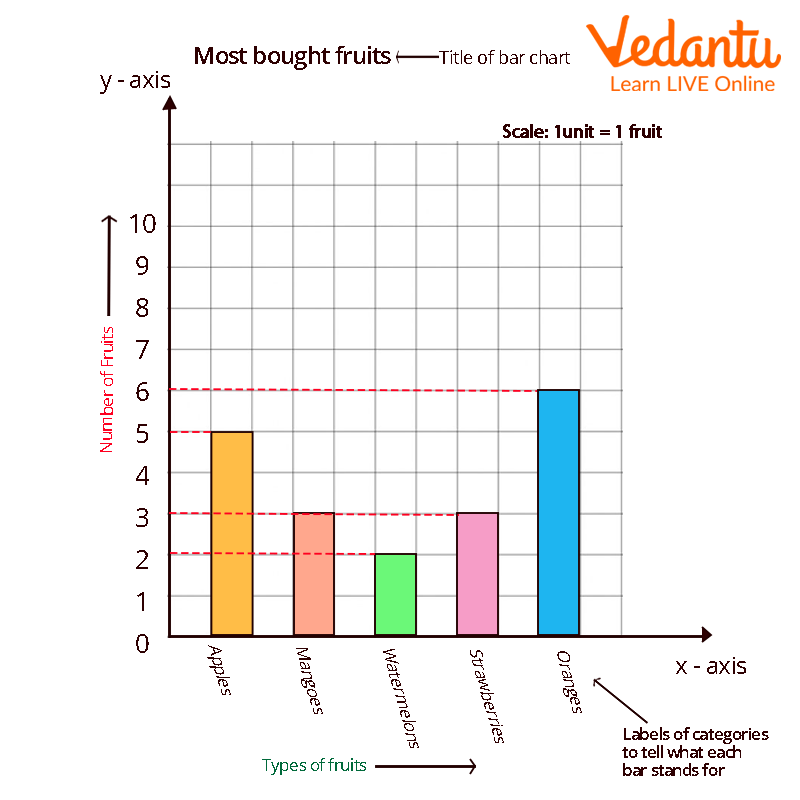
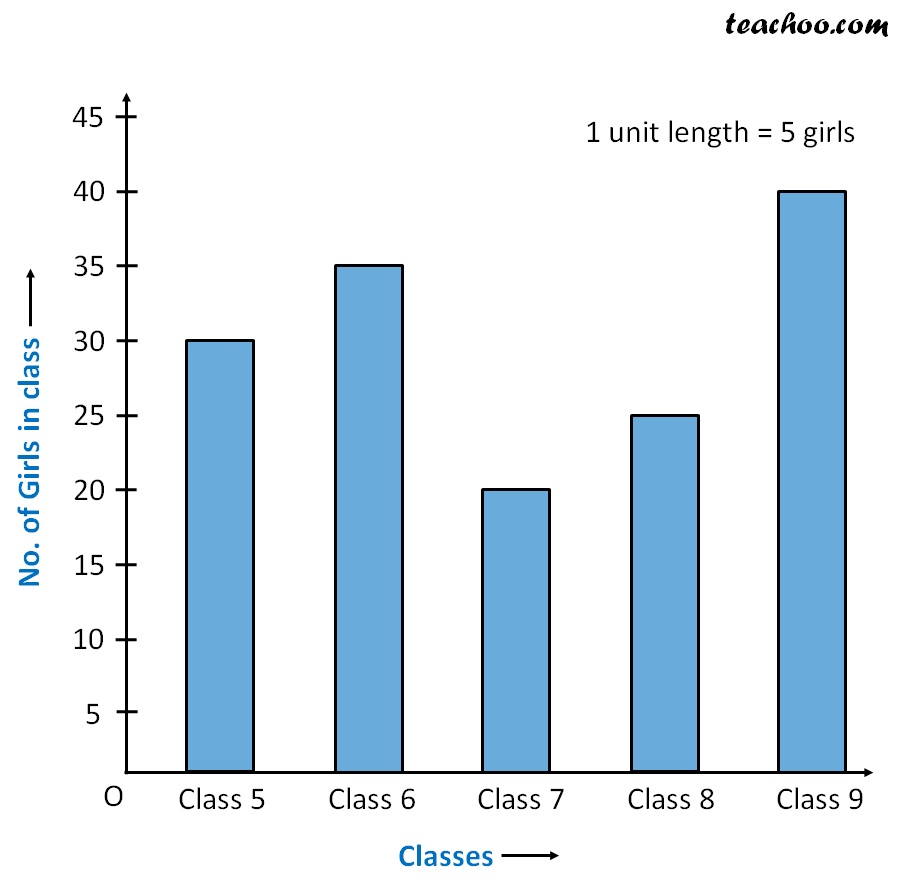
Label the horizontal x axis. In this concept, you will learn how to create and read multiple bar graphs. Each bar in this example represents a specific subcategory (like girl/boy).
A bar graph is also known as a bar chart and is used to visually represent the discrete set of data. We use to draw multiple bar charts if the total of different phenomena is meaningless. Bar graphs have three key attributes:
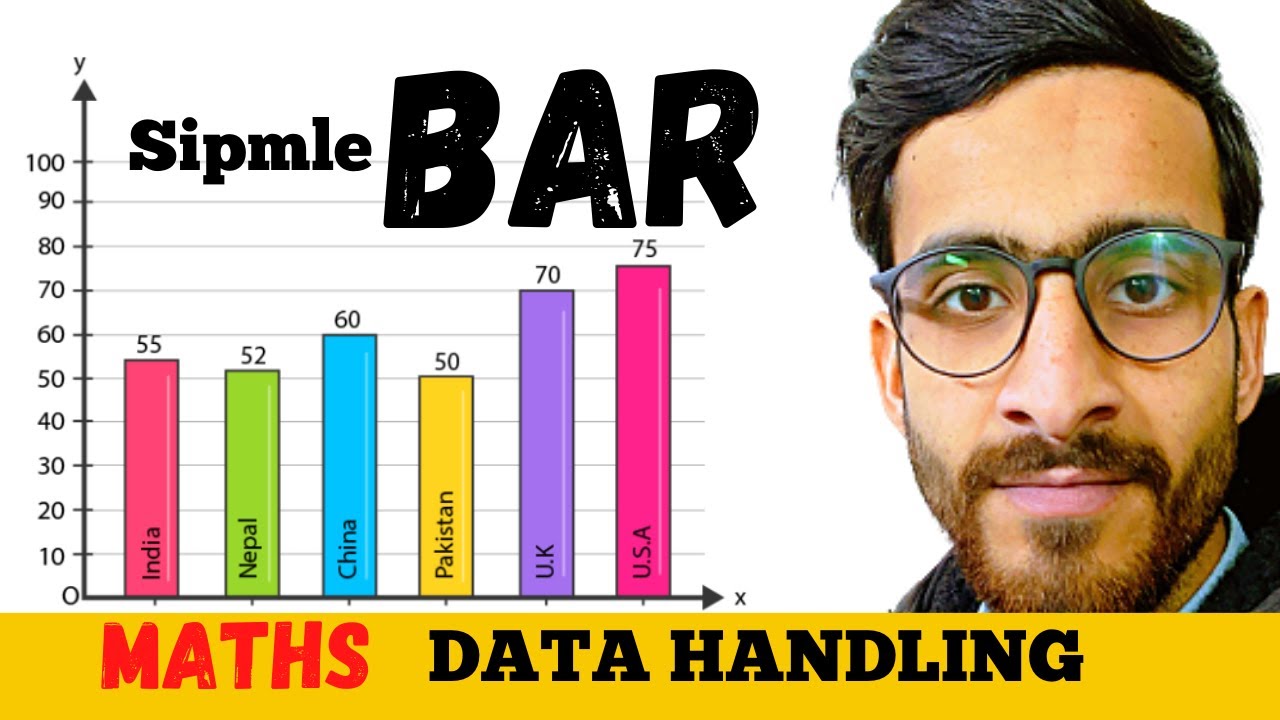
Use bar charts to do the following: Give the graph a title. A bar graph, also known as a bar chart, is a graph that uses rectangular bars to represent different values to show comparisons among categories, such as the amount of rainfall that occurred during different months of a year, or the average salary in different states.
Bar graph vs other graphs. How to draw a bar graph? Draw the horizontal (x) and vertical (y) axis.
It is inbuilt in the ggplot2 package, we don’t need to install it separately. Bar charts can also show big changes in data over time. Difference between bar graph and histogram.
Here, you will find ways to create a bar chart in excel with multiple bars using insert chart feature, adding variables & converting charts. However, each parameter must have the same unit of measurement. Look at the range in data and decide how the units on the vertical axis ( y) should be labeled.
X = [ datetime.datetime(2011, 1, 4, 0, 0), Label the vertical y axis. To create a multiple bar graph:
Advantages and disadvantages of bar. Table of content. The required diagram is given below:
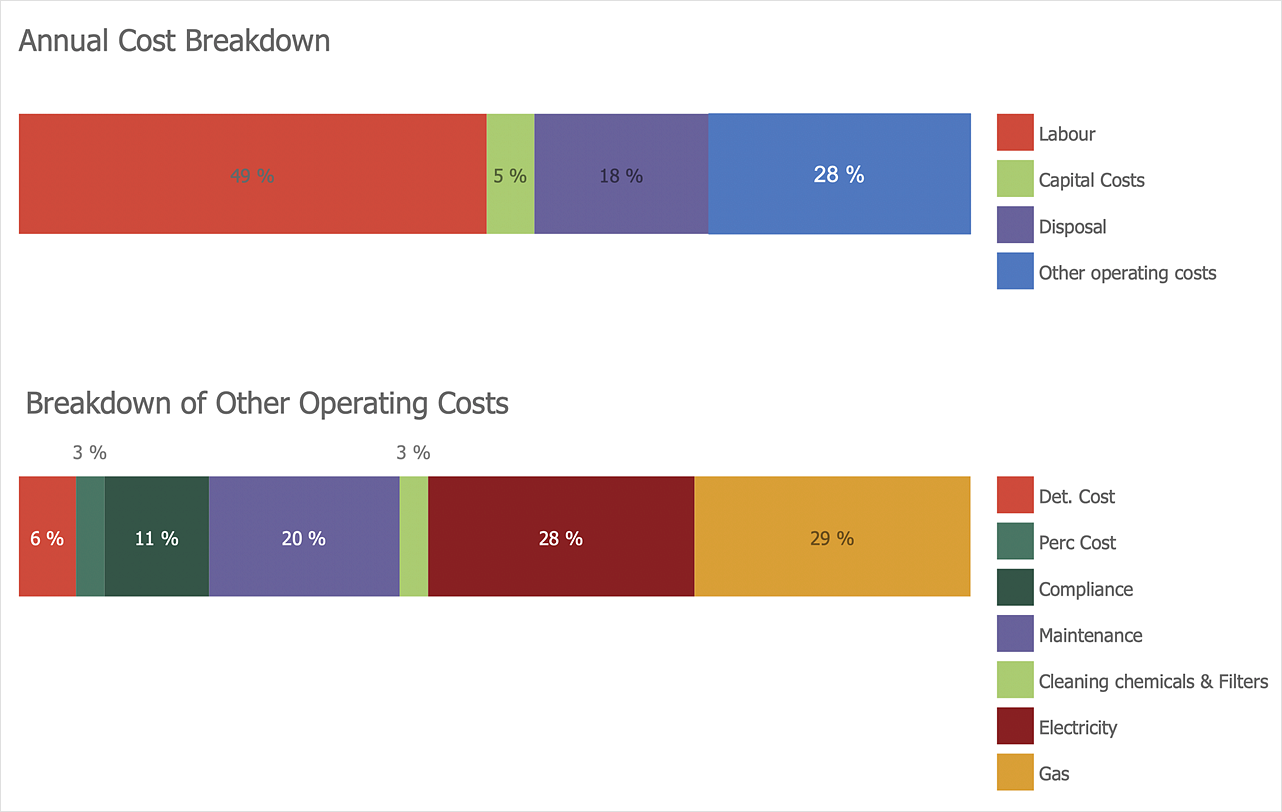
To avoid overlapping of bars in each group, the bars are shifted 0.25 units from the previous bar. A bar diagram makes it easy to compare sets of data between different groups at a glance. Using geom_bar () from ggplot2 package.