Supreme Info About What Is C V In Physics Excel Line Chart X Axis Values

The symbol c stands for specific heat and depends on the.
What is c v in physics. It is interesting to note that some physics symbols are very relatable (like “d” for distance) while some are unrelatable (like “c” for the speed of light). Cv is the specific heat at constant volume, and cp is the specific heat at constant pressure. 25 rows symbols representing physical quantities, units, mathematical operations and.
This means it is the amount of heat required to increase temperature by 1 dgree celcius, when heat is given at constant volume. The formula is : Note that bold text indicates that the quantity is a vector.
Below is an elaborate list of. Asked 8 years, 1 month ago. The molar specific heat capacity of a gas at constant volume cv is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mol of the gas by 1 c at the constant volume.
Where q is the symbol for heat transfer, m is the mass of the substance, and δt is the change in temperature. Learn what a physics major cv is and discover seven steps to help you write your own physics major cv, including a template and an example you can review. When scientists talk about refraction, they use a formula.
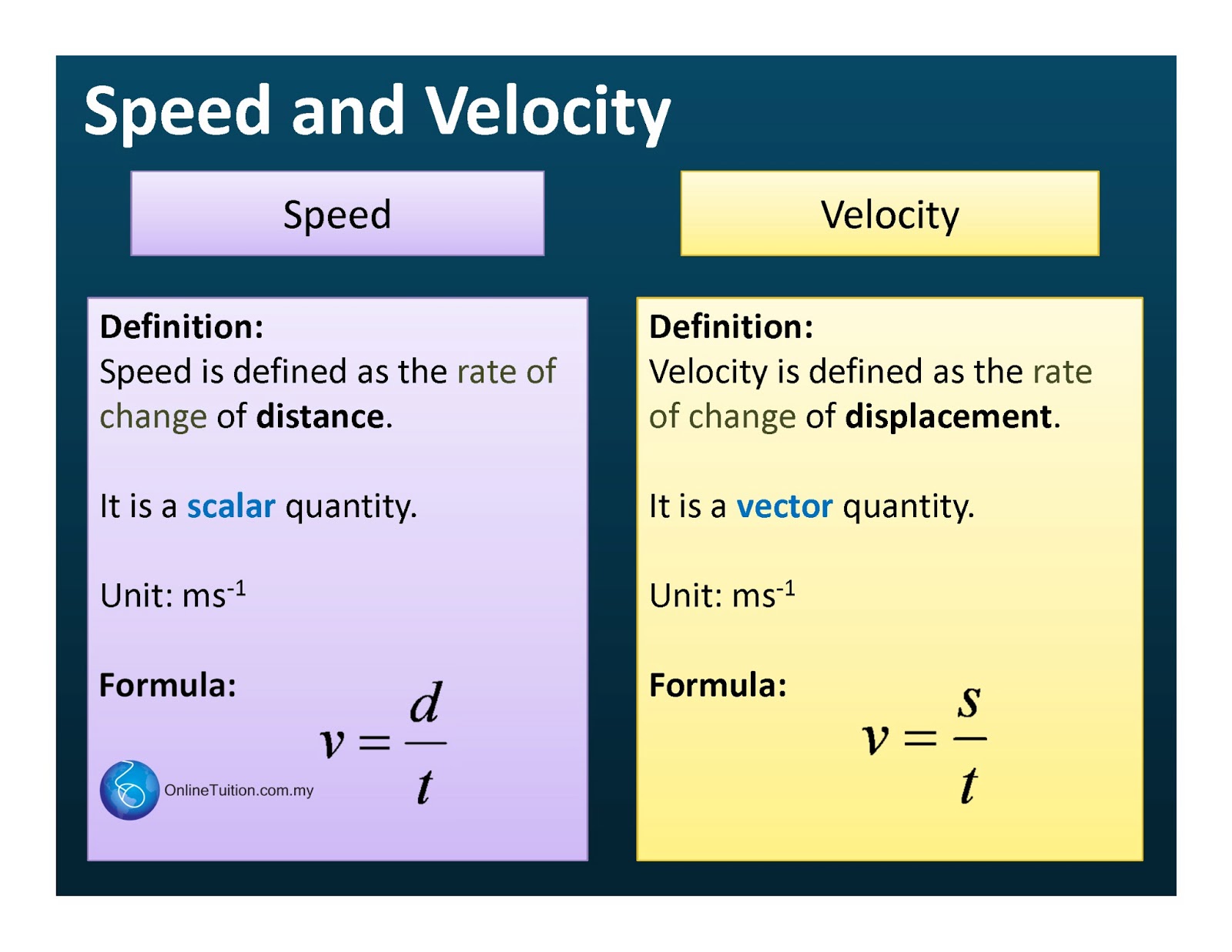
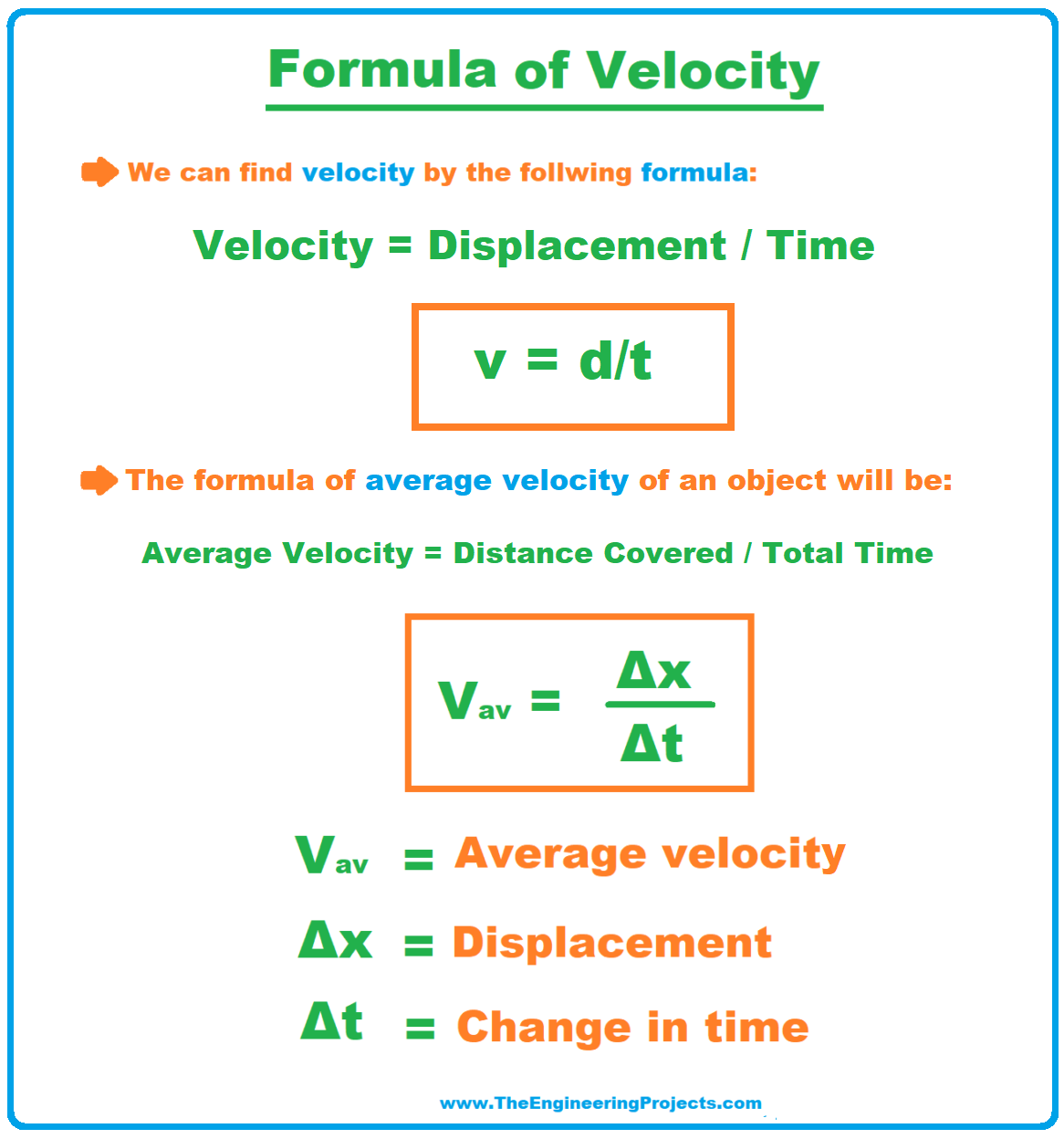
What is the difference between cp and cv in thermal physics? Choose units and enter the following: It is denoted by the alphabet c and measured using si unit m/s.
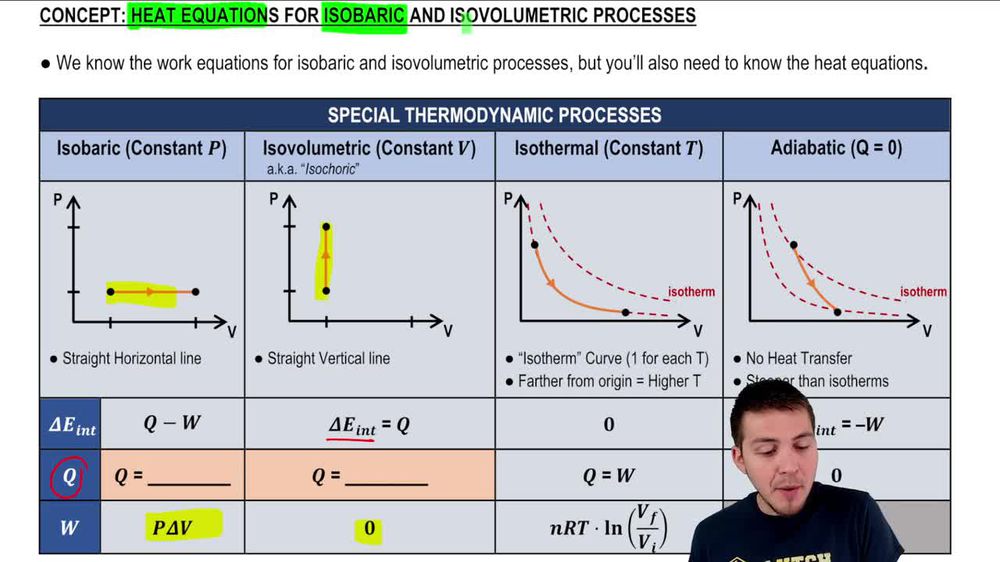
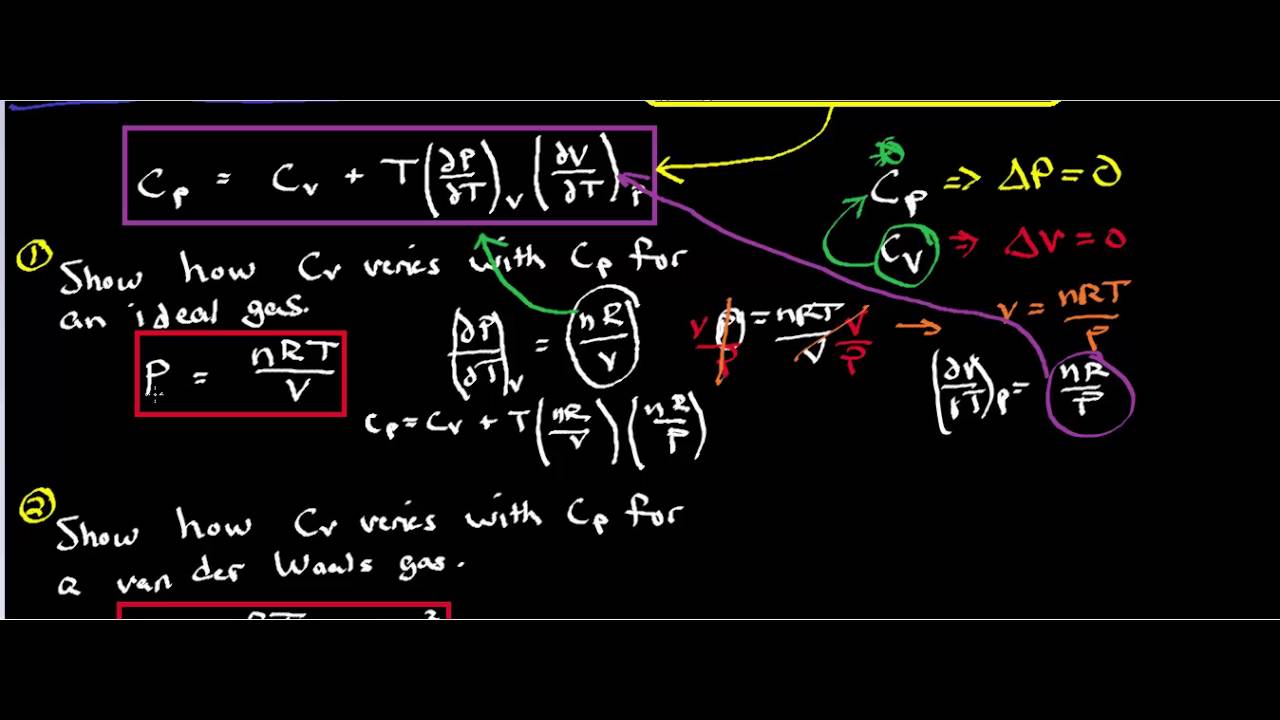
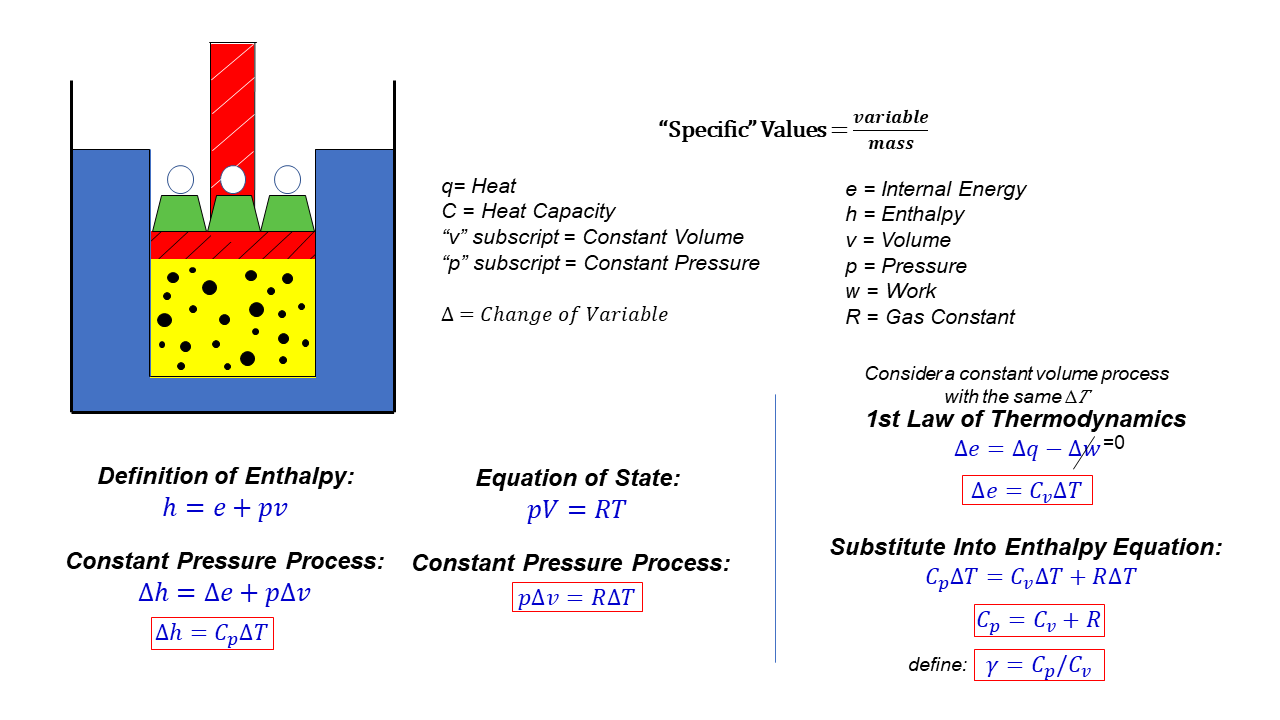
Derive the expression for the difference between \(c_p\) and \(c_v\) by beginning with the definition of \(h\), differentiating, dividing by \(dv\) (to generate the. Modified 8 years, 1 month ago. The relationship between cp (specific heat at constant pressure), cv (specific heat at constant volume), and r (gas constant) is given by the equation:
If you connect a battery across a capacitor it will acquire equal and opposite charges on its plates. Definition of molar heat capacity (c) the total amount of energy in the form of heat needed to increase the temperature of. New research suggests their youth could actually be eternal.
( q) this is the. What are heat capacity c, cp, and cv? Cp and cv are both measures of heat capacity, but they differ in the conditions under which they are measured.
Specific heat is the heat energy required to raise the temperature of. N = c / v c is the speed of light in a vacuum, v is the speed of light in that substance and n is the. These charges will reside on the facing surfaces of the.
Cv is specific heat in constant volume. $c_{v}=\frac{fr}{2}$ where $c_{v}$ is the molar heat capacity at constant volume, $f$ is the total number of degrees of freedom. Why is capacitance defined as charge divided by voltage?









![The Relation between Cp and Cv [PHYSICS] (CBSE) Class 11 YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/FZvqCZiZ0yo/maxresdefault.jpg)